Led Lamp
An LED lamp or LED light bulb is an electric light for use in light fixtures that produces light using one or more light-emitting diodes called (LEDs).
Types of Basic Purpose Bulbs
Standard LED bulbs: Standard LED bulbs spread light at a wide-angle throughout a space. You can use these for many places like night lights, reading lamps, hallways, and other general fixtures.
Can LED bulbs: These are known as recessed lights bulbs, can LED bulbs fit into sockets or cans and they are usually mounted into the ceiling.
Flood LED bulbs: Flood bulbs are meant to release a strong but wide beam of light to brighten a broad area. They’re mainly used in exterior applications and on construction sites.
Globe LED bulbs: Globe bulbs release light in all directions, making them ideal for, decorative fittings, bathroom, and pendant lights.
Types of Decorative Bulbs
Candelabra LED light bulbs: These are also known as candle bulbs or chandelier bulbs, these imitate the shape of a candle flame. They usually fit best in accent lighting, wall sconces, and decorative fixtures.
Track LED light bulbs: You can use these directional lighting, work area task lighting, or to highlight something particular such as artwork and decorative pieces.
Edison LED light bulbs: Also known as vintage bulbs, are all about aesthetics and ambiance. These are best suited for ornamental fixtures like pendant lights and modern chandeliers.
Tube LED light bulbs: You may know these also as linear light bulbs, they have a functional style designed for more professional applications like office buildings, warehouses, kitchens, and workspaces.
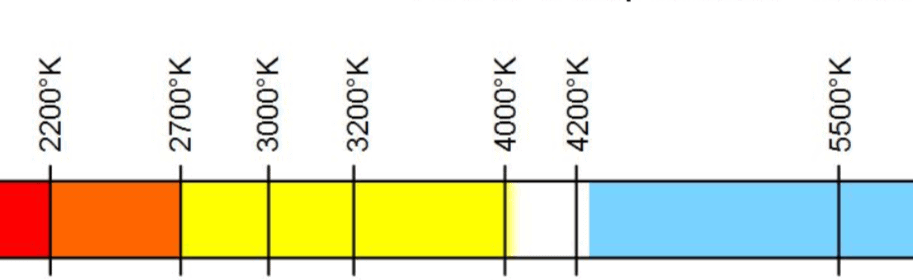
- 2000-2200K Amber light for softly lit, cozy ambiance
- 2700K Soft white light relaxing everyday light
- 3000K Bright white light for a comfortable atmosphere
- 3500K Neutral white light for fresh and crisp light
- 4000K Cool white light for a bright atmosphere
- 5000K Daylight type light for a full energy ambiance
- 6500K Super daylight for a super bright atmosphere
Other LED Light Options and Features
LED lights are not restricted to replacement bulbs. Some fixtures, including several models of ceiling fans and recessed downlights, have built-in LED lighting.
LED technology is also found in some elastic light strips or tape that can be applied as under-cabinet lights. Under-cabinet lights can be applied to add task lighting in the kitchen or to give ambiance and decorative accents in other rooms.
Holiday lighting can be substituted with LED holiday string lights that will decrease energy consumption. LED string lights also more fire-safe, because LED lights emit only small amounts of heat, in comparison to incandescent lights.
All LED lights are not dimmable, so be sure to check the packaging to find out if the bulb is compatible with dimmers.
If you want quality lights, you should look for ENERGY STAR-certified LED light bulbs, which have been tested for color tone, light output, and efficiency.
Smart LED bulbs can connect to a Wi-Fi network, or to Bluetooth to allow remote control of the lights. Features such as dimming and color-temperature tuning are usually standard features in smart bulbs. And some models don’t need a smart-home hub for control of the lights.
The lifetime of LED Lighting Products
The life of LED light bulbs is defined differently than that of other light bulbs, such as incandescent or compact fluorescent lighting. LED bulbs do not burn out. Instead, they undergo lumen reduction, wherein the brightness of the LED bulb dims slowly over a longer period of time. Unlike incandescent bulbs, LED bulb lifetime is set on a prediction of when the light output diminishes by 30 percent.
Are LED lights dangerous?
LEDs possess undeniable advantages on several fronts, including from an energy efficiency standpoint, but like most new technology, they do have their disadvantages:
- Headaches and other physical symptoms
- Toxicity of the materials
- Eyestrain or damage
- Impact on our sleep cycles
- Impact on nature
The toxicity of the materials and the impact they have on nature are documented and scientifically verified. But some of the other disadvantages like eyestrain and headaches are unconfirmed.
LEDs and Heat
LEDs use heat sinks to absorb the heat generated by the LED and dissipate it into the enclosing air. And this then prevents LEDs from overheating and burning out.
Heat control is usually the single most important part of the successful performance of an LED over its lifetime.
The higher the temperature at which the LEDs are run, the more quickly the light will diminish, and the shorter the beneficial life will be. Standard LEDs are not recommended to be used in enclosed fixtures.
For LEDs to manage heat, it can use many variations of a heatsink design. The improvement in materials has allowed companies to design LED bulbs that match the forms and measurements of regular incandescent bulbs. Despite the heat sink design, all LED products that have earned the ENERGY STAR have been examined to guarantee that they properly manage the heat so that the light output is well maintained through the end of its estimated life.
Can I use an LED bulb in an incandescent fixture?
You can use LEDs in any light fixture, but make sure it’s not enclosed or fully air-tight and is not an old-style dimmer system. Know that if you use LEDs in a fully air-tight light fixture or with a dimmer switch that is not suited for LEDs it will reduce the lifespan of the bulb.
Some LED lamps are made to be a straight compatible drop-in replacement for incandescent or fluorescent lamps.
The LED bulb packaging may explain the light output in lumens, the power usage in watts, the color temperature in Kelvin or color information such as “warm yellow-white”, “cool white” or “daylight white”, the operating temperature scale, and the comparable wattage of an incandescent lamp giving the same amount in lumens.
How is LED lighting different than other light sources, such as incandescent and Compact Fluorescent (CFL)?
LED lighting differs from incandescent and fluorescent in various ways. When designed properly, LED lighting is more economical, adaptable, and longer-lasting.
LEDs are more directional light sources, which means that they emit light in a precise direction, unlike incandescent and CFL, which release light and heat in any direction.
That then means that LEDs are capable to use light and energy more efficiently in a number of applications.
However, it also means that advanced engineering is required to create LED light bulbs that illuminate light in every direction.
Regular LED colors include amber, red, green, and blue.
To produce white light, different color LEDs are mixed or covered with a phosphor material that changes the color of the light to a common white light used in many homes. Phosphor is a yellowish material that covers some LEDs.
Colored LEDs are broadly used as signal lights and indicator lights, like the power button on a laptop.
In a CFL, an electric current flows linking electrodes at each end of a tube containing gases. This reaction produces ultraviolet called UV light and heat. The UV light is converted into visible light when it hits a phosphor coating on the inside of the light bulb.
The traditional incandescent bulb produces light using electricity to heat a metal filament until it becomes hot. And as a result, incandescent bulbs release about 90% of their energy as heat.


